Three Ways to Get an Image Inside Text
Add some pizazz to your designs with one of these easy ways to create image-filled text.

Recently, this question was posted on the InDesign forum at Adobe.com:
I’m apparently missing something that seems like it should be pretty straight forward. Working with CS3, using Vista, I’m trying to put an image “within” the structure of large bold type for a poster. I have placed an image on a bottom layer, then on another layer above that have put reversed out type (Paper swatch) within a solid block of black. The solid block of black completely covers the image on the underneath layer. I would THINK that the image below would just show through the type area but the reversed out type is just showing up as white. Am I missing something simple here?
The concept of what the “Paper” color means, exactly, can be confusing. As I replied to the writer, filling an object or text with Paper means that you want its contents to appear to knock out everything behind it, through the stacking order and through the layers, to the color of the paper upon which it’s printed. (And putting things on different layers doesn’t make a difference, so I won’t mention that aspect again.)
If you fill text with the Paper color and then print the file on brown craft paper, what looked white on screen (the default Paper color) will be brown in the printout — regardless of any other object it overlaps– because you’re supposed to see the actual paper color. This is why InDesign lets you edit the default Paper color to best match the color of the paper you’ll be printing on, so you can preview it on screen.
His question reminded me of a student’s frustration with the None color in a recent class. He wanted the exact same effect as the guy who wrote the post, and thought the solution was to fill the reversed-out type with the None color, instead of Paper. Nope — the None color just affects how the text fill interacts with the text frame’s fill, so you end up with invisible text on solid-filled text frame.
Let’s take a look at what they were trying, and then go over some ways to get what you want.
Here are two frames in InDesign (CS4, though this applies to CS3 too). One is an image, the other is a black text frame with Paper-filled text. This is what the forum poster was working with.
When you drag the text frame on top of the image (both frames are exactly the same size in this example, so I’ll offset the frame a bit), this is what you get:
If you change the color of the text to None, you get this beauty:
I swear, there’s text in there. ;-)
Okay, so those don’t work. How about some solutions?
The Knockout Group Solution
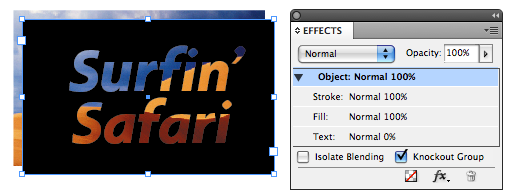
The first method that comes to mind was first explained by David in this post, which was an offshoot of a method that Pariah Burke came up with. The idea is that by 1) Making the text 0% opaque (just the text, not the object); and 2) Turning on Knockout Group (a checkbox at the bottom of the Effects panel) for the text frame, the result is that the text knocks out of the color of the text frame it’s in, but nothing else.
So anything behind the text frame can be seen through the “holes” made by the type. And the type is fully editable — very cool. Note that the Knockout Group attribute can be applied to a single frame, as above … it doesn’t have to be two or more grouped objects.
One problem with this method is that since the text is technically filled with nothing (0% opacity), you can’t apply some other effects to it that manipulate its fill color, like Bevel and Emboss or Inner Shadow. Effects that don’t need a fill, like Drop Shadow, work fine.
Since the poster specifically said that he wanted the text-filled-with-an-image to appear within “a solid block of black,” he has another method available, one where he could add any other Effect he wanted to the text.
The Multiply Frame Solution
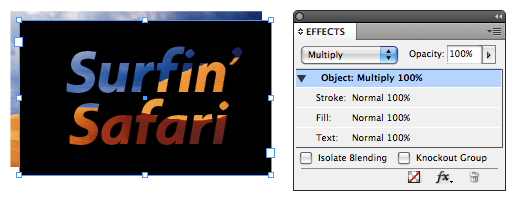
You start with two objects: The image, and the Paper-colored type reversed out of a black frame. In other words, this guy again:
Drag the text frame on top of the image, and then change the text frame object’s Blend mode (in the Effects panel dropdown menu) from the default Normal to Multiply:
Why did this work? Because in the underlying algebraic equations of the Multiply Blend mode, pure black is like multiplying by 1 — it stays the same. Pure white (or Paper) is like multiplying by 0 — it disappears. All other pixel color values fall between 1 and 0, and so you see something new when two overlapping pixels are multiplied together. (I love the math behind the blend modes.)
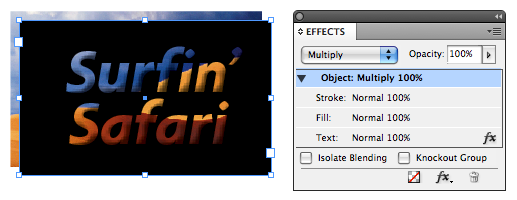
Since the text is technically 100% opaque, you can select the Text attribute in the Effects panel and apply any Effect you want to it. Here it is with Bevel and Emboss:
Because of the special properties of Black and White in Multiply Blend mode, this method only works with a solid Black text frame and Paper or White-colored text. If the text frame is filled with a different color, like green (left) or even None or Paper (right), you get this … which is pretty neat anyway.
Both of these methods, Knockout Group and Multiply Text Frame, allow you to keep the text live, so you can edit it, apply styles to it, and so on. There is another way to fill text with an image, but it requires you to convert the text to vector outlines (Type > Create Outlines), meaning it’s not longer editable. Unless you’re very very good with the Pen tool.
The Filled Text Outlines Method
You start with two objects: An image and a text frame containing the text.
First, with the Direct Selection tool (the white arrow), select the image and copy it to the clipboard (Edit > Copy).
If you want all the text in the frame to be filled with the image, select the frame with the Selection tool and choose Type > Create Outlines. (If you want to fill just some of the text in the frame, select what you want with the Type tool before choosing the Create Outlines command.) Here’s Surfin’ Safari as outlines:
Select the outlined text with the Direct Selection tool (as I’ve done above, though you don’t need to select all the points) and choose Edit > Paste Into. If Paste Into is grayed out, you’re probably using the Selection tool instead of the Direct Selection tool. Also, if only a portion of the outlined text becomes selected, you may need to select all the outlined text at once by Shift-clicking with the Direct Selection tool and then choosing Object > Paths > Make Compound Path first, to “unite” the paths into one single object.
I made a compound path out of the two lines of outlined text for Surfin’ Safari. Then I selected the compound object with the Direct Selection tool and chose Edit > Paste Into. Here’s the final result, as seen in Preview mode:
While the text itself is not editable, you can still use the Direct Selection tool (hovering the cursor inside a letterform so it turns into the Hand tool) to select the image it holds and drag it around, revealing different parts of the image inside the outlined type. You can also select the outlined type with the Selection tool and apply an Effect to it … for example, our friends, Bevel and Emboss and Drop Shadow:
This article was last modified on December 19, 2021
This article was first published on January 3, 2009
Commenting is easier and faster when you're logged in!
Recommended for you

A Visual Guide to InDesign Preferences
Use this guide to understand which InDesign preferences only affect the current...

dot-font: Making Art of Zeroes and Ones
dot-font was a collection of short articles written by editor and typographer Jo...
Format Text Automatically with Style Packs in InDesign
Learn how to effortlessly style text throughout an InDesign document with the he...